This technical blog is my own collection of notes , articles , implementations and interpretation of referred topics in coding, programming, data analytics , data science , data warehousing , Cloud Applications and Artificial Intelligence . Feel free to explore my blog and articles for reference and downloads . Do subscribe , like , share and comment ---- Vivek Dash
Monday, March 8, 2021
Friday, March 5, 2021
Dictionary Methods in Python for processing of constituent Key and Value Pair Data Objects
Dictionary
Methods in Python
* There are various methods to
process the elements of a dictionary
Methods
to process Dictionaries in Python
===================================
dict.clear()
This method removes all the
key-value pairs from the dictionary 'd' .
2) copy()
d1
= dict.copy()
This method copies all the elements
from the dictionary 'd' into a new dictionary object 'd1' .
3) fromkeys()
dict.fromkeys(s[,v])
This creates a new dictionary
with keys from a given sequence 's' and all the values set to 'v'
4) get()
dict.get(k[,v])
This returns all the values
associated with the key 'k' . If the key is not found , then it returns 'v'
5) items()
dict.items()
This returns an object that
contains key-value pairs of dictionary item 'dict' . The key value pairs are
stored as tuples in the objects .
6) keys()
dict.keys()
This returns a sequence of keys
from the dictionary object "dict" .
7) values()
dict.values()
This returns a sequence of
values from the dictionary object "dict"
8) update()
dict.update(x)
This method adds all elements
from the dictionary 'x' to the dictionary item object 'dict'
9) pop()
dict.pop(k[,v])
This method removes the key 'k'
and its associated value from the dictionary object "dict" and
returns the value associated with that key "v" is returned . If the
key is not found and "v" is not mentioned then "KeyError"
exception error is raised .
10) setdefault()
dict.setdefault(k[,v])
If the key 'k' is found , then
its value is returned and if the key is not found , then the k,v pair is stored
into the dictionary 'd'. In the given program , we are going to retrieve the
keys from a dictionary object using the keys() method . The keys() method
returns dict_keys object that contains only keys . We will be also able to
retrieve the values from the dictionary object using the values() method . This
method "values()" returns all the values in the form of a dict_values
object . Similarly , the items() method can be used to retrieve all the
key-value pairs into the "dict_items"
method can be used to retrieve
all the key-value pairs into the "dict_items" object .
==============================================
Program
A Python program to retrieve
keys , values and key-value pairs from a dictionary object
# dictionary methods - create a
dictionary with employee details
dict
=
{
'Name' : 'D001' ,
'Id' : '001',
'Salary' : 1000
}
# print the entire dictionary
print(dict)
# display only keys
print("
values in dict = ", dict.values())
# display both key and value
pairs as tuples
print("
Items in Dictionary =", dict.items())
Output
:
{
'Name' : 'D001' ,
'Id' : '001',
'Salary' : 1000
}
Keys
in dict =dict_keys(['Name','Id','Salary'])
Values
in dict = dict_values(['D001','001','1000'])
Items
in dict = dict_items([('Name','D001'),('Id',001),('Salary',1000)])
In the given program, we are
creating a dictionary by entering the elements from the keyboard and when the
user enters the elements from the keyboard inside the curly braces , then the
values inside the dictionary object are treated as key value pairs of a
dictionary by using the eval() function . Once the elements are entered , one
can find the sum of the values using the sum() function over the values of the
dictionary .
The screenshot for the used code implemented over Jupyter Notebook is given as below :
Keys and Values over Dictionary Objects in Python
Keys and Values over Dictionary Objects in Python
* Important points to remember while dealing with Dictionary
Objects in Python are the following :
1) One can use any type of datatype while dealing with any value
for a Dictionary Object in Python
2) A value can be a number , string , list , tuple or any other
dictionary object in Python
3) Keys in Python should obey the following rules
*** point-1 ***
Keys should be always unique . Duplicate Keys are not allowed in
Python . And If the user/programmer enters the same key again over the existing
dictionary , then the old key would be overwritten and only the new key would
be available . One can consider the following example for considering the case
of uniqueness of a Key in Python
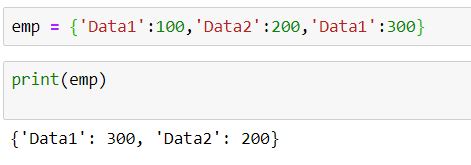
emp =
{
'Data1':100,
'Data2':200,
'Data1':300
}
If someone wants to print the contents of the dictionary object
after the object has been created , then one would find that the values within
the dictionary for the data item which has been entered twice that is
"Data1" which is entered twice in the case would be printed only once
as a single data item can only exist once , and this data item would have the
higher value of the object .
print(emp)
Result :
{
'Data1':300,
'Data2':200
}
Here , one would be noticing that the values for the data item
are replaced with the one which has a higher value over the other data item
object which means that the dictionary object gives precedence to that sub-data
item within it to exist within it which has a higher value for the same /
duplicate key .
The screenshot for the above code is as given below :
*** point-2 ***
Keys should be immutable in nature . For example , one can use a
number , a string or a tuple as key since the keys are immutable in nature .
One cannot use lists or dictionaries as Keys . If as such , Keys are used then
one will get 'TypeError' . One can consider the following example in case of a
Dictionary Object :
emp =
{
[
'Data1']:100,
'Data2':200,
'Data1':300
}
# Here , upon compilation and execution of the code one would get to see that for the list element 'Data1' we get an error in the output section . This is because, as mentioned above, the key item should only be a number , string or a tuple in nature .
An article on - Dictionaries in Python ( with example code and result of Dictionary Creation )
Dictionaries in Python
* A dictionary represents a group of
elements arranged in the form of key-value pairs .
* In the dictionary , the first element is
considered as "key" and the immediate next element is considered as
the "value"
* The key and the associated value are
separated by the help of a colon (:) operator
* All the key-value paris in a dictionary
are inserted in curly braces { }
* One can take a dictionary by the name
"dict" that contains the employee details in the following manner :
dict_01 =
{
'Name'
: 'Gareeb' ,
'Id'
: 001 ,
'Salary'
: 0000
}
* The name of the dictionary item object in
the given example is "dict_01"
* The first element in the dictionary is a
string object called "Name" and its associated value is
"Gareeb" .
The second item in the element is
"Id" and its associated value is "001" . The third object
in the dictionary object is "Salary" and its associated value is
"0000"
* The above example is that of a dictionary
object with its identifier name as "dict_01" . The dictionary item
object is holding three values within it in the form of key and value pair .
* From this , we can get to see that there
are 3 pairs of keys and values in the dictionary which can be shown in the
below figure .
* To briefly explain the process of
creation of a dictionary object , one can write a
program in the given manner :
# creating dictionary with key-value pairs
dict_01 =
{
'Name' : 'Gareeb' ,
'Id':001 ,
'Salary':0000
}
# Here a dictionary object is created with
the following items in the form of
# key-value pairs - Name , Id and Salary
# If someone wants to retrieve the
requisite values from the dictionary then one
# can do the following to retrieve the
necessary objects
print(' Name of Employee ',dict_01['Name'])
print(' Id of Employee ',dict_01['Id'])
print(' Salary ',dict_01['Salary'])
The Code and Output for the same can be
seen in the below given screenshot:
Thursday, March 4, 2021
Extended example on Rule of Cross Multiplication in Ratio and Algebra ( Notes with Example )
-
Write a program in Python to calculate the factorial value of a number When we talk about factorial of a number , then the factorial of tha...